Diamonds are known for their shine, brilliance, and beauty. Before you set out to purchase a diamond, it is important to learn what contributes to determining the value of a diamond. This not only helps you to understand how to evaluate a diamond, but also helps you to choose a diamond that would be best for your budget!
In the next section of the blog, we will explore the fundamental 4 features, known as the 4 Cs to diamonds, and learn how diamonds are evaluated based on the diamond 4 Cs. Find out more about the 4 C's to a diamond here:
What are the 4Cs?
The 4Cs refer to the universal standard of assessing the quality of any diamond. It was introduced by the Gemological Institute of America in the 1940s and is also known as the GIA 4Cs. The 4Cs are: cut, color, clarity, and carat. To determine a diamond's value, you can measure each of the Cs through their own scales. Read the next section to learn more about which one is the diamond four C's most important value, and the 4 C's of diamonds explained.
The 4Cs of Diamond Quality
The quality of every diamond can be evaluated through the diamond 4C guide. Here's the diamond 4Cs explained:
Diamond Cut
The diamond cut refers to the brilliance and sparkle of a diamond. The cut of a diamond is regarded as the 4 C's diamonds most important value. The facets of a well cut diamond would be able to reflect light excellently. A diamond's cut quality determines the fire, scintillation, and brilliance of the diamond. If you see a dull diamond, then that means that it is a poorly cut diamond. You should note that the diamond cut determines the proportions of a diamond, and not the external outline. It should not be confused with the shape of a diamond.
The diamond cut grades of the GIA 4Cs chart are: poor, fair, good, very good, and excellent. Diamond cuts are evaluated based on the diamond cut grade, from excellent to poor. The quality and price of the diamond increase based on the quality of the cut.
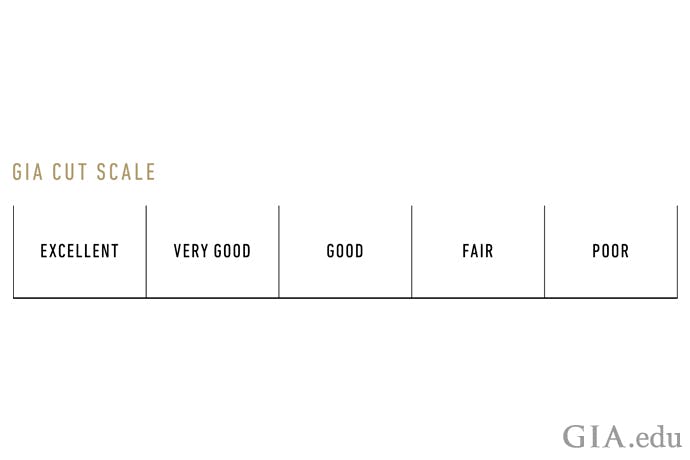
Diamond Color
The diamond color evaluates the absence of color within a diamond. Colorless diamonds are rarer than diamonds with yellow or brown hues. Expert gemologists evaluate the color grade through careful inspection under controlled lighting. This allows them to spot the presence of color that may not be visible to the naked eye. Diamonds with colors like blue or pink are known as "fancy colors" and are evaluated with a different diamond color grading system.
In the 4 C's chart diamond for the color grading system, white diamonds are evaluated based on a 23-shade scale from "D" to "Z", with "D" having the highest rarity within the scale. Meanwhile, AGS uses the 0-10 color grading system, and the IGI also uses the D-Z color grading system.
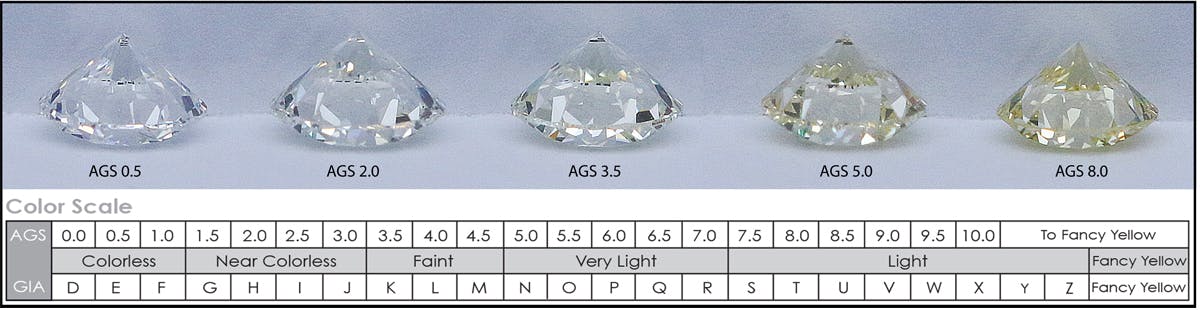
Diamond Clarity
A diamond's clarity refers to the absence of inclusions and blemishes within a diamond. The higher the clarity of a diamond is, the less presence of inclusions and blemishes there will be. Inclusions refer to the internal flaws present within a diamond, while blemishes refer to the external flaws. Both of the characteristics can influence how the light is refracted within a diamond, even if they are not visible to the naked eye.
The GIA diamond grading system uses a scale with 11 different grades. Usually, you won't be able to spot inclusions within a diamond without special equipment from grade VS and higher. Below is the GIA clarity scale from diamond 4 C's explained.
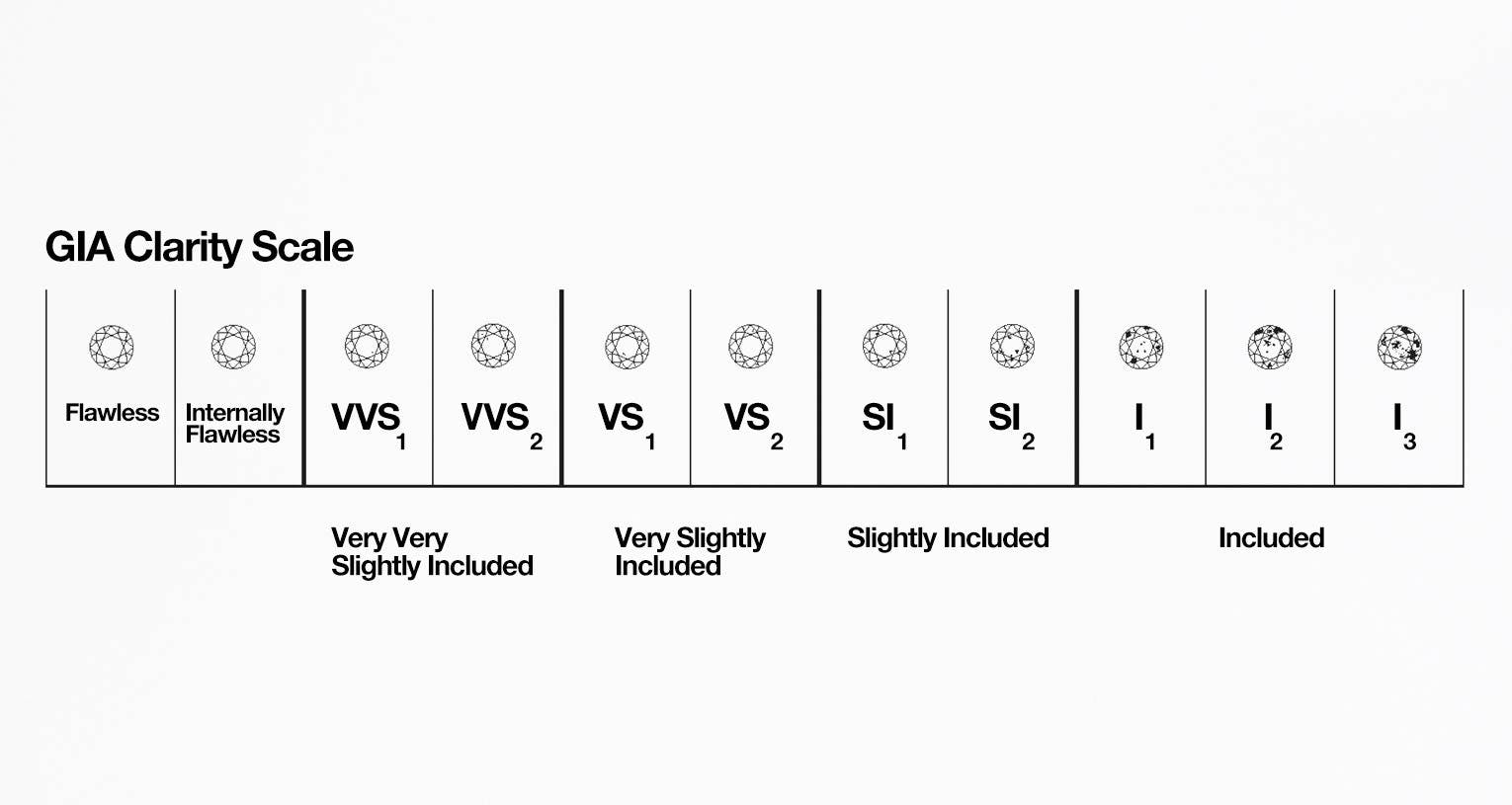
Diamond Carat
The diamond carat refers to the weight of the diamond. It should not be confused with the size of the diamond. It directly influences the price of a diamond. The carat weight may vary in different diamond shapes. For example, a round brilliant diamond of 0.5 grams will not look the same as an emerald cut diamond of 0.5 grams.
In the carat measurement system, 1 carat = 200 milligrams. The following image is the carat measurement system of the IGI 4Cs of diamonds explained!

Types of Diamonds
Before you buy a diamond, we also recommend that you know more about the difference between natural and lab-grown diamonds. This can help you guide your purchase decision alongside the 4 Cs of diamonds chart:
Natural Diamonds
Natural Diamonds Vancouver form deep within the Earth's crust, under extreme conditions of heat and pressure. Volcanic activity brings them to the surface through a type of volcanic rock formation called kimberlite pipes. These pipes contain only 5 percent of diamonds, which are then mined through special equipment. Unlike lab-grown diamonds, these are much rarer to find. This makes the value and price of natural diamonds higher than lab-grown diamonds.
Lab-Grown Diamonds
Lab Grown Diamonds Vancouver are produced in a highly controlled laboratory environment. While lab created diamonds are grown within a laboratory, they have the same chemical and physical properties as natural diamonds. These are real diamonds that are evaluated using the same 4 Cs chart. They are also known for being a more ethical and environmentally friendly alternative to natural diamonds.
Conclusion
The four Cs are integral to assessing the quality of a diamond. This helps us to identify quality diamonds by determining its value through different grading systems and scales.
Searching for Beautiful Diamonds to Symbolise your Eternal Bond?
Find the perfect diamond for your special occasion. Browse through SMC Diamond's collection today!

